Vincoli unità di carico
Introduction
This section allows you to define and manage the physical constraints associated with the different types of load units used in the system (e.g., pallets, packages, containers). The constraints configured here are essential to ensure compatibility between goods, handling equipment, storage spaces, and shipping rules. Each constraint can impact logistics planning, automatic load validation, and exception management.
Configuration
1. Click on the Load Unit Constraints item under the Service Parameters item in the Marketplace section .
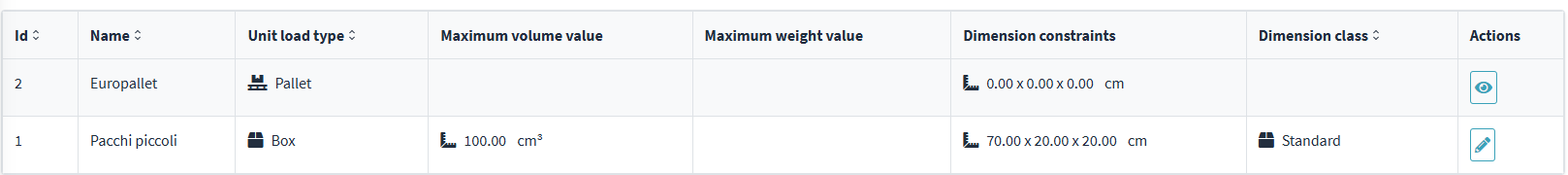
2. Once you enter the page, the table displays the list of currently configured constraints. Each row represents a load unit type.
3. Each configurable constraint is composed of a series of fields that define the operating characteristics of the load unit. Below is a description of each field:
- Id : Unique identifier of the constraint, automatically generated by the system.
- Name : Descriptive name of the loading unit (e.g. Euro pallet , Small parcels ).
- Load unit type : Category of the unit, selectable from the list (e.g. Pallet , Package ).
- Maximum Volume : Maximum volume allowed for the unit, expressed in cubic centimeters (cm³).
- Maximum permitted weight : Maximum permitted weight, expressed in kilograms (kg).
- Size Constraints : Maximum dimensions of the unit (Length x Width x Height), expressed in centimeters.
- Size Class : Operational classification of the unit (e.g. Standard , Oversize ), useful for groupings and loading rules.
- Actions : Icons to edit ✏️ or delete 🗑️ the constraint directly from the table.
4. Click on Add Load Unit Constraint 
5. In the Name field , enter a descriptive name for the loading unit (e.g., Euro Pallet , Small Parcels ). It must be clear and recognizable in reports and dashboards.
6. In the "Loading unit type" field , you can select the category best suited to the goods you want to manage. Each option represents a logistics type with specific operational characteristics:
- Pallet:
Ideal for bulky and stackable loads. Standard in warehouses and palletized transport. - Envelope:
Used for documents or small, flat items. Suitable for lightweight, trackable shipments. - Generic package
format for medium-sized shipments. Widely used by couriers. - Crate:
A rigid container, often made of wood or plastic. Highly protective for fragile or valuable goods. - Flexible container bag
for granular materials, textiles, or food. Non-stackable. - Large bag:
A variant for bulky and loose loads. Requires care when handling. - Barrel
Used for liquids, powders, or chemical materials. Requires specific safety constraints. - Full truckload
: A load unit dedicated to an entire vehicle. Used for direct shipments. - Partial truckload
refers to a shared shipment on a single vehicle. Useful for optimizing transportation costs. - ISO 20 Container:
A standard 20-foot container. Used in intermodal transport (sea, land, and rail).
7. In the "Size Class" field , you can assign a size label to the load unit. This classification is essential for:
- Apply different loading rules
- Optimize storage
- Facilitate traceability in reports and audits
The available options are:
- Small:
For compact, lightweight items, such as envelopes or small packages. Ideal for mailing, e-commerce, or documentation. - Standard:
Intermediate category, suitable for most regular-sized packages, crates, and pallets. It is the most commonly used class in ordinary logistics flows. - Oversized
For bulky, heavy, or unconventionally sized units (e.g., containers, special loads). Requires special attention during handling and transportation.

8. In the constraint creation form, you can specify the three main dimensions of the load unit. These values are essential for:
- Calculate the actual volume
- Check compatibility with vehicles and shelving
- Assign the size class correctly
The fields to be filled in are:
- Longest side in cm
Enter the maximum length of the unit. This value represents the longest side and affects handling and storage. - Average side in cm
Enter the average width of the unit. This is useful for calculating horizontal space and pallet or shelf placement. - Shortest side in cm
Enter the minimum height of the unit. This value is often crucial for stacking and stability.
9. Additional Description is a free field for operating notes, technical specifications, or internal references. It may include codes, regulatory references, or usage instructions.

10. Click Save All and Close to finish. 