Servizio di Magazzino
Introduction
The “ Warehouse Service” section allows customers to view, insert, modify and manage logistics services relating to warehouses not owned by them , but managed by third-party companies .
This section is dedicated exclusively to registering external services and should not be used for internal warehouses.
2. To access, click on the Warehouse Service item in the Marketplace section in the left menu.
3. The main screen displays a table with the following fields:
- Id : a unique identification number automatically assigned to the service.
- Code : an internal code that identifies the service, useful for traceability (example: WR-34).
- Service Name : The name assigned to the service, which may correspond to the function or type of warehouse.
- Warehouse Name : The specific name of the warehouse associated with the service.
- Country : The country where the warehouse is located, accompanied by a national flag icon.
- City : the exact location of the warehouse.
- Service Type : The classification of the service offered, for example “managed warehouse”.
- Surface area (m²) : the available area of the warehouse expressed in square meters.
- Actions : A column that includes icons for editing or deleting the service. The edit icon updates the service's data, while the delete icon permanently removes it.

Warehouse Service Supply Configuration
1. Click on the Add Service button at the top right 
2. In the Service Name field, enter the identifying name of the warehouse service (e.g. Magazzino Centrale Milano ).
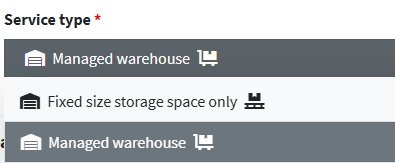
3. The Service Type field defines the warehouse usage model. The available options are:
- Managed warehouse: comprehensive warehouse management service, suitable for companies requiring an operational warehouse with centralized logistics management.
- Warehouse space: This is a physical space rental service only . It does not include management, handling, or shipping, and the company handles logistics operations independently. It's suitable for those looking for storage of their products without additional services.
4. In the Warehouse Information field, enter the name you want to use to identify the warehouse (e.g. Northern Italy Logistics Hub ).
5. In the Company field , enter the name of the company to which the warehouse belongs.

6. In the Free Address Search search field, you can start typing the address and select it from the Google Maps suggestions list, and the subsequent data will be filled in automatically using a Geolocation map.
7. In the Email field , enter the warehouse's reference email address. This is used for operational and administrative communications.
8. Fill in the Telephone field with a valid telephone number to contact the warehouse directly.
9. You can add more information in the Notes field.
10. In the Storage Characteristics section, the warehouse's operating capacity is defined :
Maximum storage area (m²): Indicate the available floor space for storing goods. Value in square meters (m²).
Maximum storage volume (m³): indicate the total available volume, also taking into account the useful height of the warehouse. Value in cubic meters (m³).
Maximum number of pallets (n.) indicate the maximum number of standard pallets that can be stored at one time.

11. In the Maximum Acceptable Size fields , enter Length / Width / Height (cm). Enter the maximum measurements (in centimeters) the warehouse can handle for each package or load unit.
12. In the Maximum weight per unit accepted field, define the maximum weight that can be stored or moved per single unit (e.g. pallet, package, container).
13. The Predominant Storage Type drop-down menu is used to identify the primary way in which goods are managed and organized in the warehouse.
The available options are:
- Pallets: Goods are stored on standard pallets (e.g., 120x80 cm EUR pallets). Typical of warehouses with automated handling or forklifts.
- Shelving: Goods are stored on shelves or racks . Used for small items or split orders.
- Bulk goods stored without standard packaging units , directly in the available space. Typical for raw materials, granular products, rolls, or bulky goods.

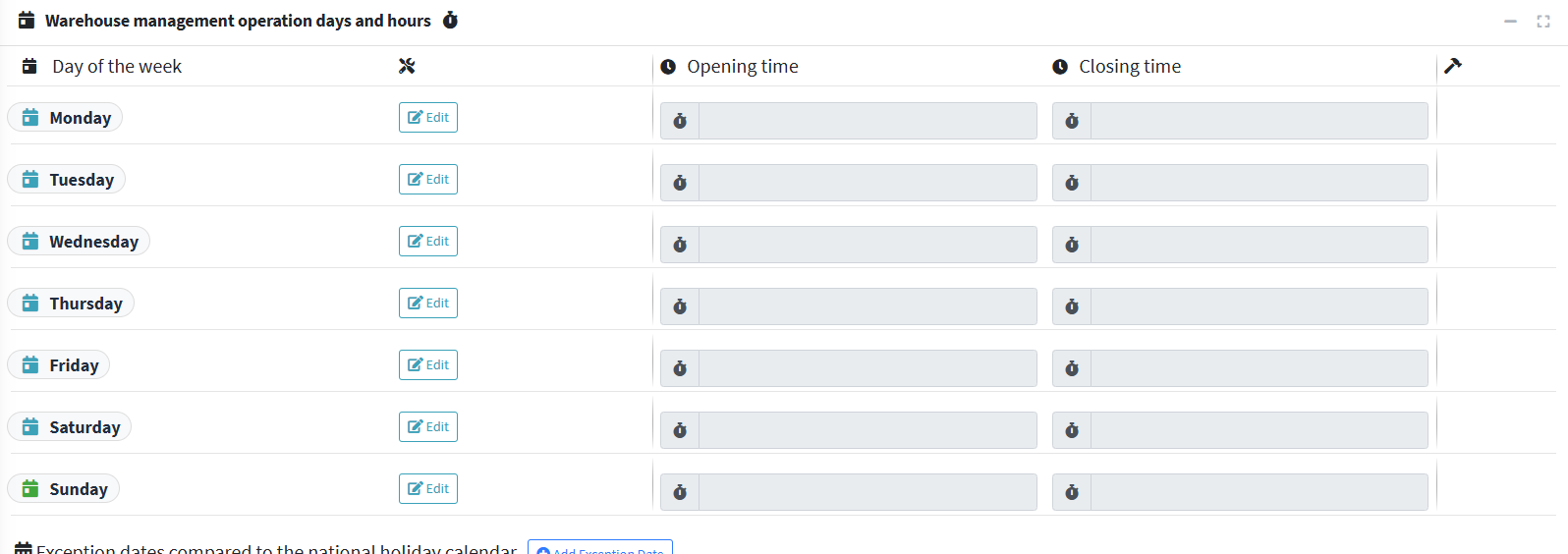
14. In Warehouse Management Operating Days and Times, set the warehouse's weekly calendar.
- Day of the week you can select the opening days (Monday to Sunday).
- Opening/Closing Hours: After clicking Edit , enter the start and end times (e.g., 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM). You can change the hours for each day. You can leave this field blank for days when the warehouse is closed.
- Dates with exceptions to the national holiday calendar can be added (extra holidays, extraordinary closures, exceptional openings). Button: Add Date with exceptions .
15. The Temperature and Humidity Control section is used to specify the types of goods the warehouse can handle, based on storage, safety, and value requirements.
16. In the Commodity Type drop-down menu , choose from the following options:
- General merchandise: products without specific storage requirements. Examples: consumables, office supplies, standard industrial goods.
- Perishable goods are products with a limited shelf life that require rapid handling. Examples: fresh food, flowers, and produce.
- Refrigerated goods: Goods requiring temperature-controlled storage (2°-8°C). Examples: dairy products, medications, and soft drinks.
- Frozen goods: Goods that must be stored at temperatures below 0°C. Examples: meat, fish, frozen foods, ice cream.
- Dangerous goods: goods subject to specific regulations (ADR, IMDG, IATA). Examples: chemicals, flammables, explosives, corrosives.
- Bulky or heavy goods are products with non-standard dimensions or weights. Examples: machinery, industrial components, construction materials.
- High-value goods : Products with a high economic value that require additional security measures. Examples: jewelry, electronics, luxury goods.
- Waste or goods for disposal: materials intended for treatment or disposal. Example: WEEE, industrial waste, special waste.
- Sensitive materials – Confidential goods requiring confidentiality and data protection. Examples: classified documents, paper archives, media.

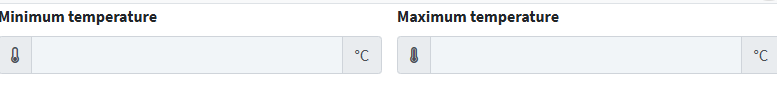
17. In the Minimum Temperature field, enter the lowest value (in °C ) that the warehouse can guarantee.
18. In️ Maximum temperature enter the highest value (in °C ) that the warehouse can guarantee.
19. In the Material Handling Equipment section , there are options describing the accessibility and tools present:
- Heavy duty scale for weight control.
- Warehouse accessible by truck with direct access for road haulage.
- Crane for lifting and handling very heavy or bulky goods.
- Trailer parking area dedicated for loading/unloading heavy vehicles.

21. In the Security Features you can select protection and control elements:
- Fenced courtyard
- Surveillance cameras
- Fire prevention system
- Burglar alarm
- Controlled access (badge, code, etc.)
- Continuous security monitoring
- Security service

22. In the Certifications section, select the certifications held by the warehouse, which are important for ensuring quality and regulatory compliance:
- ISO 9001 → process quality.
- ISO 14001 → environmental management.
- ISO 45001 → health and safety at work.
- HACCP → food safety.
- AIB International → international food standards.
- BRC → safety and quality in the supply chain.
- MHRA → approval for pharmaceutical products.
- Organic Food Federation / SOIL / Organic Farmers and Growers → organic certifications.
- CBP Supply Chain Security → supply chain security.
- UKWA → membership of the UK Warehouse Workers' Association.
- C-TPAT (Customs Trade Partnership Against Terrorism) → partnership for the international security of goods.

23. Click Save Warehouse Service to finish. 
Creating a rate for a warehouse service
1. The system allows you to configure a rate associated with a specific logistics service within a third-party managed warehouse.
2. Click on Rates in the Actions menu

5. The page displayed in the interface shows the list of rates applied to the services offered within the selected warehouse. Each line represents a specific service, with detailed information useful for configuration and customer consultation.
For each service the following are shown:
- Code: service identifier, useful for internal traceability.
- Service Description: The name of the service offered, such as “Labeling,” “Receiving Goods,” or “Returns.”
- Pricing model: how the cost of the service is calculated (e.g. “€0.50 LQ”, “€10.00 one-off”, “€3.00 per piece”).
- Price: economic value applied according to the pricing model.
- Constraints: Any conditions applicable to the service, such as the type of merchandise ("Clothing and Shoes & Bags"), the validity period ("October - December 2025"), or the package size ("Small Packages"). If not present, the field is blank.
- Available actions: icons that allow you to modify or delete the rate associated with the service.
6. The navigation bar provides quick access to the main operational functions of the logistics management system. Each section represents a distinct phase of the goods movement cycle.
- Goods Receiving: Access to incoming goods registration and acceptance functions.
Typical uses : supplier unloading, quantity checking, location assignment. - Shipping: Managing outgoing and delivery operations.
Typical uses : order preparation, printing shipping documents, assigning couriers. - Returns: Functions dedicated to managing returned products.
Typical uses : returns acquisition, quality control, replenishment, or disposal. - Warehousing: Access to internal storage and management of goods.
Typical uses : placement, internal transfers, inventory. - Additional Services: Configuration and management of additional services.
Typical uses : labeling, kit assembly, insurance, special processes.
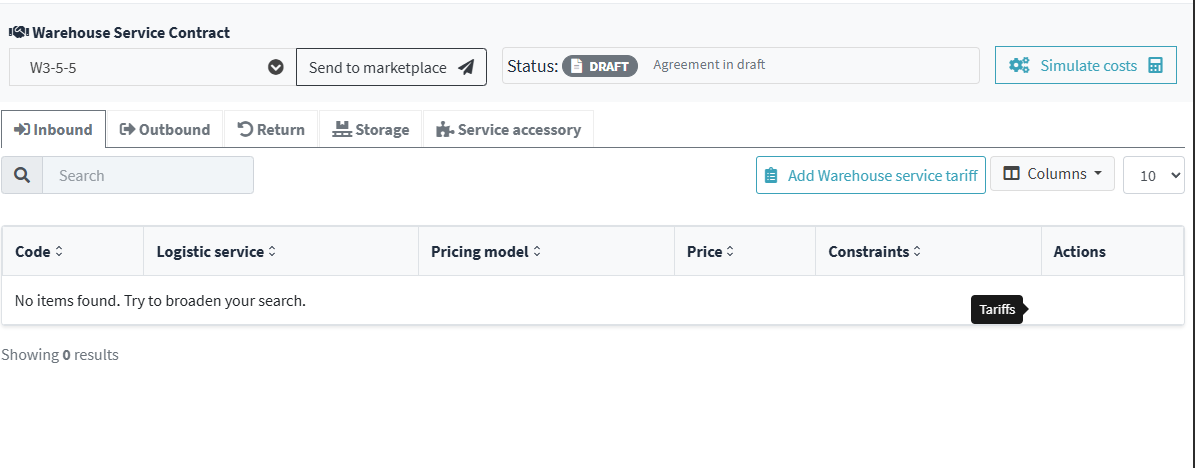
7 Click Add Warehouse Service Rate to configure the pricing parameters 
8. Use the Logistics Service drop-down menu to select the type of service to associate with the rate.
9. When configuring a rate for a logistics service, the system requires the selection of a Pricing Model , which defines the logic with which the cost of the service will be calculated. This choice is essential to ensure consistency with the type of business performed and contractual requirements.